Search Engine Optimization is undoubtedly a broad scope. On top of keyword research, content optimization, and link building efforts, webmasters also need to make sure that their sites’ technical health is fully optimized. No matter how solid your content marketing and link building efforts are, if your pages are not crawled and ranked, your SEO campaign will all be in vain.
In this article, let’s talk about the importance of technical SEO and how to make sure that you’re cracking the code.
What is Technical SEO?
Google mainly does three things: crawl, index, and rank pages. Technical SEO is essentially about making sure that these three steps are done without a glitch. On top of ensuring crawlability, it also involves all other technical aspects including speed and security.
In essence, technical SEO mainly focuses on code-level deployment of your website to enhance crawlability and ensure a healthy link structure. This way, indexing becomes quicker and more extensive.
It’s important to note that Technical SEO is not a one-and-done activity. It’s an ongoing process of maintaining your website’s technical health and being on top of Google’s algorithm updates for ongoing optimization.
Google Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
Before we go for a deeper dive about technical SEO, it’s important to first understand how exactly search engines crawl, index, and rank pages.
Crawling
Google is not automatically alerted whenever new pages are created on the web, so it has to actively find them. Google uses a piece of software called Google crawler (also searchbot, spider) to discover new pages and content to add to its database. All search engines have their own set of crawlers. Google specifically has 15 different types of crawlers, with the main one being known as Googlebot.
Once Googlebot discovers a new page, it loads and visualizes everything including the HTML, JavaScript, third-party code, and CSS. It will then determine the page’s relevance and importance, and if it passes the indexing criteria, it will index the page for future use.
Indexing
All of the pages indexed by Google will be added to its extensive inventory of websites where it draws from to provide search results to users. However, there’s no guarantee that crawled pages will be indexed.
Google assesses both the relevance and quality of a page before deciding whether or not to index them.
To meet Google’s quality and relevance criteria, make sure to:
- Focus on content quality– If the page has low-quality content (e.g. duplicated, thin, or doesn’t meet Google’s guidelines), it may not be indexed.
- Help Google understand pages’ relevance– Aim for a well-structured website with clear internal linking to help Google understand and index pages. Internal links are the pathways of crawlers, so it helps to make the most of them.
- Address technical issues– Technical errors like issues with robots.txt, 404 status codes, and incorrect redirects can all impede the indexing process.
- Make sure there are no noindex directives: Pages with noindex meta tag or nofollow attribute may be crawled but not indexed.
You can check the indexing status of your website’s pages via Google Search Console or by performing the site: operator in Google Search (e.g., site:example.com).
Ranking
If Google is a giant librarian, indexing is the cataloguing process—organizing every page on the internet like books on a shelf. Ranking, on the other hand, is how it recommends the best ones to readers. And just like a skilled librarian, Google tailors those recommendations based on the user’s interests, behavior, and intent.
Ranking happens in milliseconds and starts when a user enters a search query. Google will browse its giant index and look for the most high-quality and relevant content based on user and content factors.
The higher a website is ranked, the more relevant Google believes that site is to the query. If your pages are not ranking, it could be that:
- Your site is brand new and hasn’t been crawled yet.
- Your site isn’t linked to from any external websites.
- Your site’s navigation makes it hard for robots to crawl effectively.
- Your site contains some basic code called crawler directives that is blocking search engines.
- Your site has been penalized by Google for spammy tactics.
Both quality issues and technical site errors can get in the way of the crawling, indexing, and ranking process. To create quality and strategic content, you need to do on-page SEO right and nail down your SEO strategy. To make sure that technical errors are not holding your site back, you should be on top of your technical SEO checklist.
List of Crawling and Indexing Errors
Technical SEO is foundational because even if you have the best content, if optimization and configurations are poorly done, your visibility is bound to take a hit. Crawl errors prevent pages from being discovered, which means they can’t be indexed and won’t appear in search results.
Here are the most common technical errors you should watch out for:
1. Robots.txt Errors
Before a search engine visits any page on a domain, it will open the domain’s robots.txt file. This is a plain text document located in the site’s root directory which lets the search engines know which URLs they are allowed to visit (and which ones they’re not).
A robots.txt file can really come in handy if you want to:
- Prevent indexing of unwanted or duplicate content
- Protect sensitive pages like admin and login access
- Improve site performance by reducing server load
- Help search engine easily find your sitemap
- Control crawl budget so Google can focus indexing the most important content
While a robot.txt can be very useful, you need to be careful when setting it up as any mistakes may seriously harm your website. You may accidentally block search engines from accessing and indexing your entire site or critical parts of it. If you notice a drop in search engine visibility, consider checking your robots.txt configuration.
Checking for robots.txt errors should be routinely done, especially after making website updates, adding new pages to your site, and updating your robots.txt setting. You need to confirm if the intended access rules are in place and no accidental restrictions occur.
Common causes of robots.txt issues include:
- Not placing the file in the root directory
- Blocking important pages or resources (scripts/stylesheets)
- Incorrect disallow syntax (e.g., missing “/” or wildcard misuse)
- Using unsupported directives like noindex
- Forgetting to include the sitemap URL
When you are confident that robots.txt is behaving as desired, you can try to get your site recrawled as soon as possible.
2. DNS Errors
DNS errors may be due to web hosting issues or user-side problems, but many causes are also due to technical SEO misconfiguration like incorrect/missing DNS records; canonical URL issues, or misaligned server settings. Signs of DNS errors include websites not loading properly or displaying error messages like “DNS server not responding”. You can confirm a DNS issue using tools like nslookup.
3. Broken Links
Broken links are hyperlinks that point to pages that no longer exist. These can include external articles that have been removed or internal pages that were deleted or moved without proper redirects. Broken links not only hurt user experience but could also lead to missed SEO opportunities, as they waste crawl budget and can diminish your site’s authority.
4. Redirect Chains and Loops
A redirect chain is when there are too many redirects in a row, and a redirect loop is when the redirects just go in circles. This creates an endless cycle that prevents the page from loading and typically causes browser errors. Affected pages won’t be accessible to search engines, which lead to indexing issues, wasted crawl budget, not to mention poor user experience.
5. 5xx Errors
These are server errors that prevent the page from loading. Common server errors include:
- Internal server error (500): This is typically a temporary message indicating an issue on the web server side, but it can also point to certain misconfigurations like faulty scripts, incorrect file permissions, or server resource limits being exceeded.
- Bad gateway error (502): Server overload is one of the main causes of this type of error. Make sure to contact your hosting provider or check your themes and plugins as too many of these add-ons may also be causing the problem.
- Service not available error (503): You can see this error if your server is undergoing maintenance. You can’t do anything to directly fix it except to wait for a few minutes or hours and contact support if the issue still persists.
- Gateway timeout error (504): This error appears when one server doesn’t get a timely response from another server. It could be due to server connectivity issues, DNS changes, faulty firewall configurations, or errors in your website’s code.
These server errors can slow a website’s crawl rate, hindering the discovery and indexing process. Take note that Google may remove URLs with persistent 5xx errors from its index, so make sure you stay on top of these issues before they escalate.
How to Find Crawl and Indexing Errors
You can identify crawl errors via Google Search Console. Just go to Crawl Stats under Settings. However, technical SEO covers an even broader scope, which also includes website speed, mobile-friendliness, and even security.
Manually keeping tabs on all these errors and weaknesses can be a laborious and time-consuming task. A more efficient way to watch out for trouble spots is using an SEO auditing tool like SEO Checker. It’s an all-in-one tool that allows you to scan your website in one go and efficiently identify all SEO, speed, and security problems.
Read our full guide on How to Use SEO Checker.
Just install the SEO Checker extension, enter the website you want to scan, and in just a few seconds, you’ll get a full report of everything you need to address in terms of on-page SEO, technical SEO, speed, and security optimization.
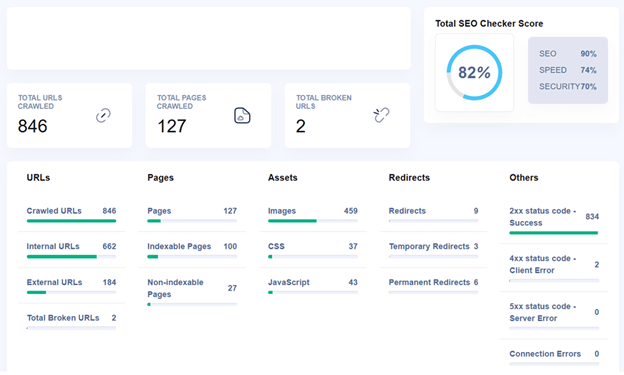
There’s a further breakdown for each category. Just click on the items with no green check marks to view what exactly went wrong.
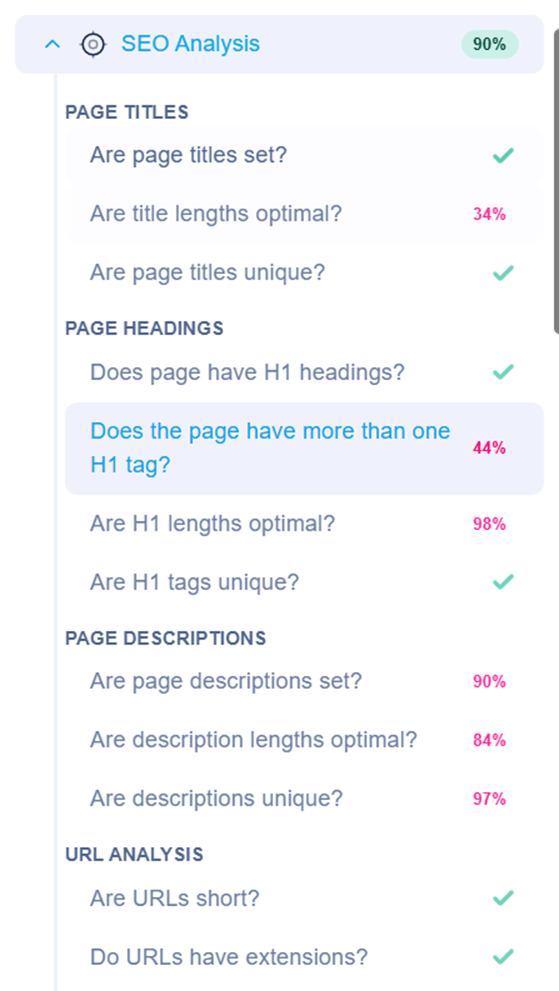
And if you don’t know what to do, there’s a guide on how you can address each error to keep your website in tip-top shape.

The goal of technical SEO is to make your website easy to navigate and free of any technical issues that hinder the crawling and indexing process. It’s not just a one-time activity but an ongoing process to steadily optimize and maintain a website’s technical foundation.
Overall, SEO can really be a rewarding pursuit, but it’s not easy and has a lot of moving parts. Thus, make use of all strategies and tools that can make your SEO process more efficient and effective.
If you still haven’t, perform a technical SEO audit now using SEO Checker. Address all blockers, then keep building momentum with your on-page and off-page SEO strategies.
Keep on refining your SEO campaign and improving your website performance– audit, optimize, repeat. With the right strategy and consistent effort, you can head in the right direction and keep climbing those SERPs.


