With the popularity of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, digital marketers now have more things to think about. We’re no longer just optimizing pages for search engines but for generative models as well.
As marketers adapt to this shift, it’s important to understand the mechanisms behind how generative models pull information. One of the concepts gaining attention in this space is the idea of fan-out queries.
What Are Fan-out Queries?
When you input a prompt on ChatGPT, it doesn’t treat it as a standalone request. It “fans out” the initial prompt into a number of related and more specific sub-queries.
If browsing is manually enabled or the question simply benefits from information on the web, ChatGPT will automatically search the web using not just the given prompt but a number of other sub-queries to generate a more specific and comprehensive answer.
For example, if you input a prompt ‘best laptops 2025’, ChatGPT will not just scour the web for such a given search term but use other keywords to establish more depth and breadth.
It would use other relevant search terms like:
- best gaming laptops 2025
- best macbook 2025
- best ultrabooks 2025
- among other keywords
The model essentially uses multiple queries to perform multiple searches. Google is also predominantly using this method to power AI Overviews and AI Mode. In fact, Google coined the term “fan-out” queries, and ChatGPT technically has no official name for it. It’s just one of the many sophisticated algorithms that enable the model to come up with the best and most satisfactory response.
The big question is, how would you know which ‘fan out queries’ ChatGPT is using? Introducing the newest feature of Keywords Everywhere.
How to Use Keywords Everywhere to Find Fan Out Queries
You can now optimize your content further as Keywords Everywhere helps reveal these hidden query variations on ChatGPT.
Step 1: Make sure that the Keywords Everywhere extension is installed and turned on before you perform the search. Check our starter guide if you’re not yet subscribed to the tool.
Step 2: Change the setting to ChatGPT 5- Thinking Model. You need to have a Plus or Pro account to use this feature.
Step 3: Activate the web search option. ChatGPT automatically searches the internet in response to queries about recent information, but manually activating the browsing option ensures that it really performs the full fan-out process.
Step 4: Input your prompt. You can input the keyword/topic you want to target and see what other queries you can use for your content and GEO strategy.
For example, if you input ‘cheap laptops’, Keywords Everywhere will show fan-out queries ChatGPT is using to search the web. You can consider targeting these queries as secondary keywords or support pages.
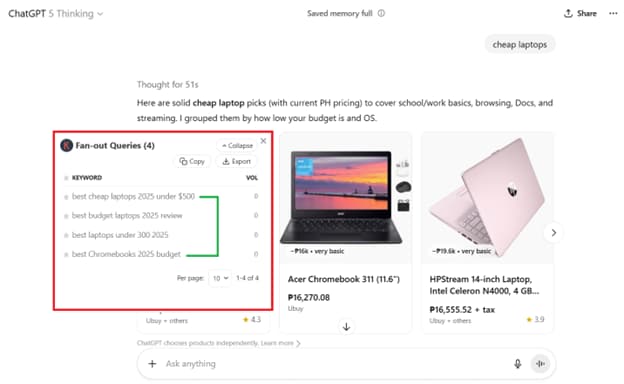
As you continue using this feature, you may notice how ChatGPT typically and intentionally scours certain high-authority websites for answers:
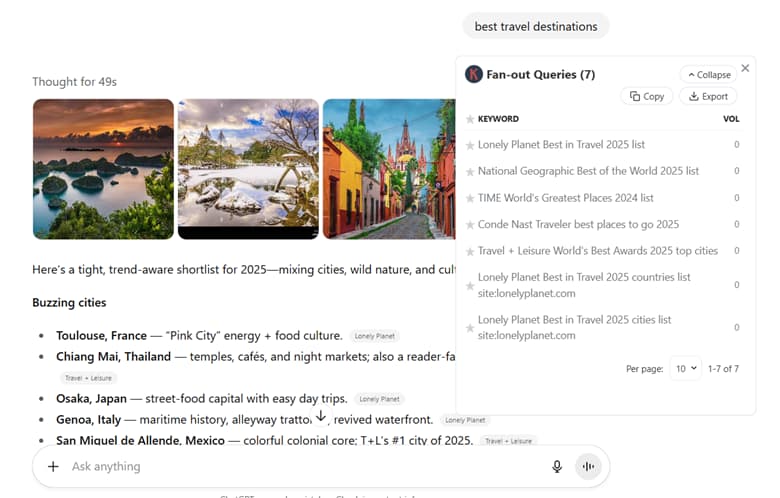
ChatGPT is designed to prioritize sourcing first-hand experience, authoritative sources, and verifiable information. There’s no harm in doing the same when producing your own content. You can even intentionally (yet naturally) mention the brands ChatGPT is seemingly leaning on for trusted information.
Keywords Everywhere’s Fan Out Queries widget is available to both free and paid plans. However, if you want instant access to search volume, you should have an active paid subscription.
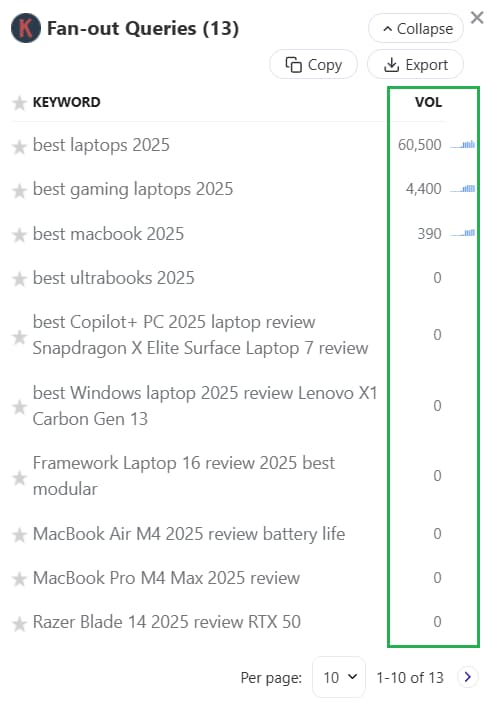
There are other tools that show fan-out queries on ChatGPT, but they typically don’t include search volume data.
Why Does ChatGPT Fan Out Queries?
ChatGPT makes use of a sophisticated multi-source approach, reducing dependence on any single search provider while providing accurate contextual answers.
Instead of just tackling one angle and interpretation, AI models fan out queries to provide richer responses that anticipate what people might ask next. Catering to users’ explicit and implicit desires helps achieve the goal of keeping users within the search experience.
This then makes AI systems act like actual research assistants, issuing multiple layered queries simultaneously on behalf of the user to generate more comprehensive and hyper-relevant content a single search wouldn’t be able to pull off.
Besides the ability to draw new conclusions, another critical function of the fan-out method is to ground AI-generated responses. Grounding is the measure of connecting an AI response to verifiable, real-world data. Unfortunately, AI hallucinations are still a problem. It’s when LLM generates credible-sounding but factually incorrect responses. Fan out queries help create direct connections to live, factual sources, helping make AI outputs more tethered to reality. The final generated output is often accompanied by links and citations to the source pages from which the information was drawn.
And it’s not just ChatGPT. Google is actively and fervently moving beyond the limitations of simple keyword matching. Instead, it’s becoming more set on fulfilling the user’s underlying, often unstated, intent with more context-rich, synthesized responses.
GEO-centered Keyword Targeting (AI SEO)
There’s a plethora of keyword research tools to support SEO, but AI keyword research tools are still emerging and evolving. Knowing what fan-out queries ChatGPT is using is a great way to get into the model’s mind and pick better topics that indicate value and demand.
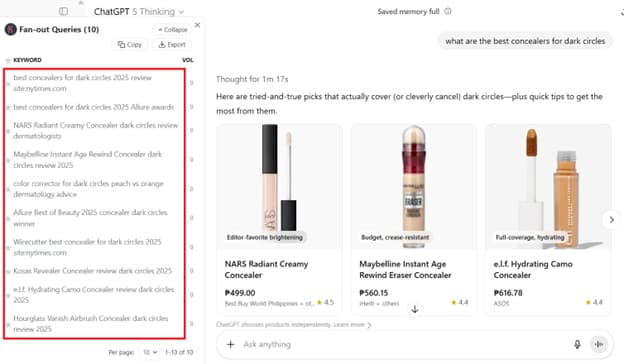
If you look into how ChatGPT fans out queries, you would notice how it intentionally looks up well-known brands and sources. This is also something you could consider; that is, making your topic coverage even more granular. For instance, instead of just covering the topic ‘best concealers for dark circles’, you can make titles more branded and even cover individual product review posts. For searches with commercial or transactional intent, ChatGPT typically looks up ‘reviews’ to better support outputs.
Although our tool does show the Search Volume of the fan-out queries, this doesn’t mean ChatGPT factors in search demand. In fact, you may notice how lots of the layered queries have zero search volume. That’s mainly because the model is more oriented toward accurately inferring intent.
In the example above, where the intent is mainly to complete a buying journey, ChatGPT will focus on product discovery, suitability for related conditions (e.g., dark circles or sensitivity), ingredient education, brand comparisons, and application advice. The fan-out queries listed would then be a mix of different terms that help the user make more informed purchasing decisions.
Fan Out Queries and Search Engines
Google was actually the one who popularized the “query fan-out” label in 2025 and applied it prominently in its AI-powered search features, particularly in AI Overviews and AI Mode. This works alongside their related patent work called ‘thematic search’.
“AI Mode isn’t just giving you information—it’s bringing a whole new level of intelligence to search. What makes this possible is something we call our query fan-out technique. “
Google I/O 2025 keynote speech | Head of Search Elizabeth Reid
So, if a user types in a particular query like “best coffee maker,” Query Fan-Out would generate sub-queries like: “How to choose a coffee maker”, “Coffee maker reviews 2025, “Drip vs espresso machine comparison, “Budget-friendly coffee makers, and “Coffee maker maintenance tips”.
This might seem like just another enhancement, but it’s actually a seismic event, forcing businesses and marketers to fundamentally rethink their SEO strategies.
Interestingly, the concept of “fan-out” and query-expansion patterns actually predate Google. In the mid-1990s, metasearch engines like MetaCrawler simultaneously extrapolated user queries across multiple search engines and synthesized results. (Erik Selberg et al, 1995)
This sophisticated mechanism has opened new doors beyond simple query matching and into a more expansive and anticipatory search experience. Generative and search engines are no longer just directories of information but synthesizers of answers. This shift has significant implications for users and businesses alike.
What Does This Mean for Marketers?
Ranking for a single keyword is no longer enough. Marketers should be ready and willing to provide useful content around many sub-queries.
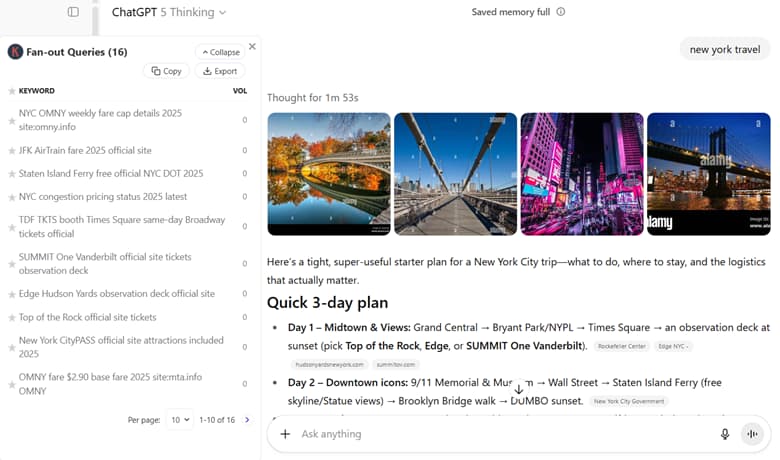
For example, instead of just targeting a query like “New York Travel”, you need to go more granular and target sub-queries like “best places to visit in New York,” “business trip in NY”, “New York flights”, “nyc subway map”, “staten island ferry schedule”, and other more more comprehensive and hyper-relevant content ideas.
Leverage Keywords Everywhere to get a better sense of how AI delves deeper into the web and use those insights to your full advantage.
As marketers, on top of improving SEO ranking, we now have to think about increasing the chances of AI brand mentions and AI citations. We have to embrace the fact that AI is now influencing consumer decisions more significantly than ever. AI adoption is only bound to increase, and the only way forward is to constantly adapt, experiment, and refine.
How to Optimize for Fan-Out Queries (AI SEO)
We’ve already established the importance of covering various facets of a topic and fulfilling more complex user intents. Let’s further hone in on what that looks like in practice and explore other ways to optimize for fan-out queries.
1. Focus on Semantic Infrastructure
If you want to naturally nail this component, your key priority when producing content should be ‘depth’. That means exploring subtopics, related questions, and making the overall coverage as comprehensive as possible. Gone are the days when cramming keywords was enough. To win in both SEO and GEO, you need to optimize for meaning, context, and intent.
2. Prioritize Structured Data and E-E-A-T Rigorously
To ensure maximum visibility, you need to cover both machine readability and human credibility. Structured data covers the former, and E-E-A-T sorts out the latter.
Especially now that more and more generic AI content is being dumped on the internet, trust signals are no longer optional. If you want to be cited more in AI-generated answers, you need to show that you’re a reliable and credible source. Some of the actionable things you can do include publishing author bylines, citing credible research, and showcasing your firsthand experience.
Beyond this, structured data and schema markup add the explicit semantic context machines require. Together, these elements strengthen your authority signals, making it easier for both search engines and AI models to identify, trust, and surface your content above weaker alternatives.
3. Cover Topic Clusters
Content is no longer evaluated just on its own merits. The goal is to make sure it fits into a much larger reasoning chain that AI models construct to address complex prompts. Don’t just strive to be present for a keyword, but strive to show up across an entire topic cluster. This involves creating a central pillar page to cover a broad topic and then developing support pages that cover more specific aspects of that topic. Internally linking these articles can further help create that well-structured network of content that supports topical authority.
4. Excel with “Zero-Click” and “Citation-Based” Visibility
Marketing has entered a whole new ballgame. Success is no longer measured only by clicks and traffic. Visibility within AI answers now counts as a win on its own. When your brand appears in these responses, it signals authority and builds consideration, even before a user clicks through.
5. Focus on the North Star
Your central focus should be on the bottom line which primarily boils down to leads and conversions. SEO is no longer just about rankings but is becoming an actual function of business development. From initial strategy to campaign monitoring, start embracing new principles hinged on your bottom line. For example, instead of focusing just on the CTR, dwell time, and bounce rate, start looking at properly tracking sentiment and mention frequency in AI responses.
Conclusion
The industry is constantly seeing new revelations changing what we know and how we think about optimizing for AI. Although GEO is still in its infancy, more and more tools are helping identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
Keywords Everywhere’s fan out queries can be a great tool to start going beyond page-level performance and into topic-level visibility and citation frequency.


