The demand for large language models (LLMs) is booming right now. Businesses across industries are discovering how useful they can be.
From improving customer service with chatbots to powering virtual assistants, LLMs are changing the way we use AI.
In 2025, this trend doesn’t seem to be slowing down. LLMs are getting even better at understanding and generating human-like language.
This opens up exciting possibilities for innovation.
In this article, we’ve pulled together some important LLM usage stats. These stats include LLM market size (across different countries), capabilities, regional adoption, and what’s next for this game-changing technology.
What is LLM?
A large language model (aka LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can understand, generate text, and perform similar tasks.
These models are known as “large” because they are trained using huge amounts of data.
LLMs are based on a kind of machine learning known as a transformer model, which helps them process and understand text.
Simply put, an LLM is a computer program that has been shown enough examples to learn how to recognize and understand human language or other types of complex data.
Many LLMs are trained using text gathered from the Internet — sometimes millions of gigabytes worth.
However, the quality of the data is important, as better-quality data helps the LLM learn language more accurately. For this reason, some LLMs use specially selected data that’s been carefully chosen.
LLMs use deep learning, a type of machine learning, to understand how characters, words, and sentences fit together.
Deep learning involves analyzing large amounts of data to spot patterns, allowing the model to figure out content differences without human help.
Once the model is trained, it can be fine-tuned for specific tasks.
This means that it can be adjusted to answer questions, generate responses, or translate text into different languages.
Now let’s take a look at some top LLM stats:
General LLM Stats
Large language models have been around since 2017. With each new version, they’ve become better at their tasks and faster at processing language.
Starting in 2022, models like LLaMA, Bloom, and GPT-3.5 became more accurate and reliable in their results. This has led to a boom in the large language model market.
Now that you know what LLMs are, let’s take a look at some of the most important LLM usage stats to give you an idea of how this technology is performing worldwide:
1. The global LLM market is forecasted to grow dramatically, from USD 6.4 billion in 2024 to USD 36.1 billion by 2030. This increase is projected at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33.2%.
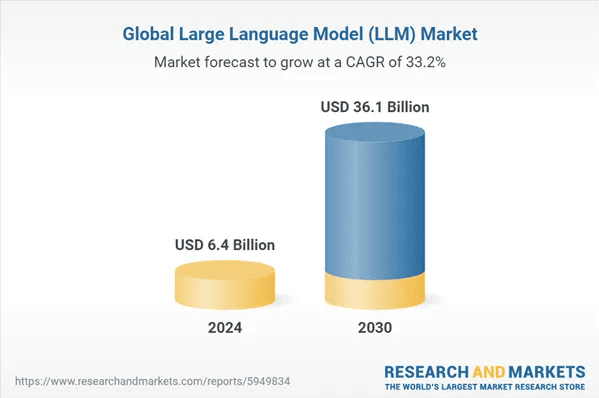
Global LLM market size 2024
2. In North America alone, the LLM market is projected to hit $105.5 billion by 2030, with a growth rate of 72.17%.
3. In 2023, Claude 3 Opus was the leading LLM tool worldwide, with an average performance of 84.83%. Close behind was Gemini 1.5 Pro, with an average of about 80%.
4. In 2023, the top five LLM developers were responsible for around 88.22% of the market’s revenue.
5. By 2025, it’s estimated that 750 million apps will be using LLMs.
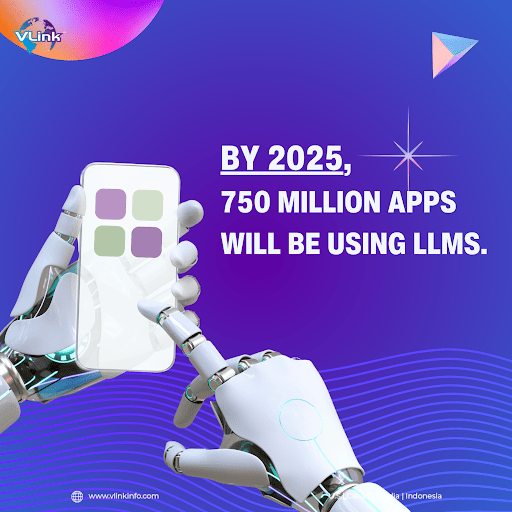
Adoption of LLM by applications in 2025
6. In 2023, younger generations, like Gen Z and millennials, along with people with higher education, higher incomes, and full-time jobs, were the most likely to recognize how AI could improve their lives. Men and women had similar expectations in this area.
7. According to Statista, over 40% of people in many countries believed that AI could help them complete tasks faster and improve their entertainment options in 2023.
8. By 2025, it’s expected that 50% of digital work will be automated through apps using LLMs.
LLM Usage Stats
LLMs are proving to be incredibly versatile, benefiting nearly every industry at every stage of its processes. This is especially true as new, customized, interconnected LLM tools are making it easier for businesses to adopt and monetize generative AI capabilities.
As technology evolves, LLMs are expanding beyond text-based tasks.
Once generative AI creates new text, audio, images, or videos from a wide range of data sources, a trained LLM can understand how to apply these AI-generated outcomes in a business context.
LLMs have the potential to boost and enhance the power of generative AI, making it more predictive, adaptable, and intelligent.
Here are the top LLM usage stats showing how industries, businesses, and individuals are embracing this technology:
9. According to Iopex, 67% of organizations are using generative AI products powered by LLMs to work with human language and produce content.
10. As of 2024, over half of global companies are planning to use LLMs (LLama models), while 26% are opting for embedding models like BERT. Only 7% are looking to use multi-modal models.
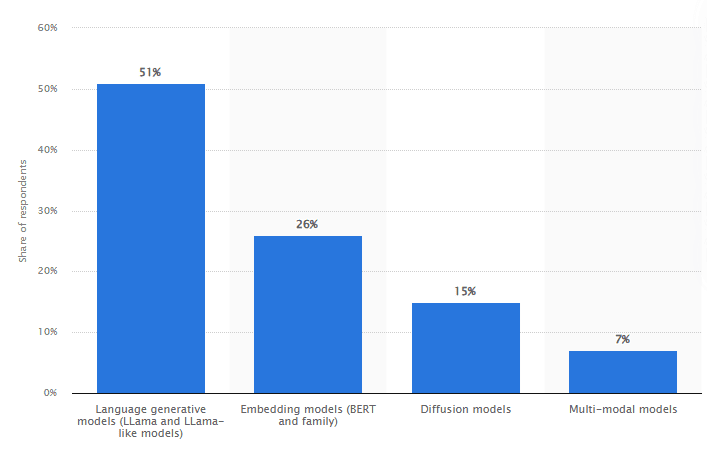
Choice of LLM models for commercial deployment
11. An Amperly AI survey found that 37.3% of respondents use AI chatbots daily in their work, while 46.0% use them a few times weekly.
12. Another survey by Amperly AI revealed that 88% of respondents said using LLMs improved the quality of their work. Research also shows that people with lower skill levels benefit most from AI.
13. Students often use LLMs to revise their knowledge, and models can be fine-tuned to generate customized quizzes and tests. This approach has led to a 62% improvement in test scores, according to Knewton.
14. In healthcare, 21% of organizations use LLMs to answer patient questions and operate medical chatbots, and 18% apply them for biomedical research.
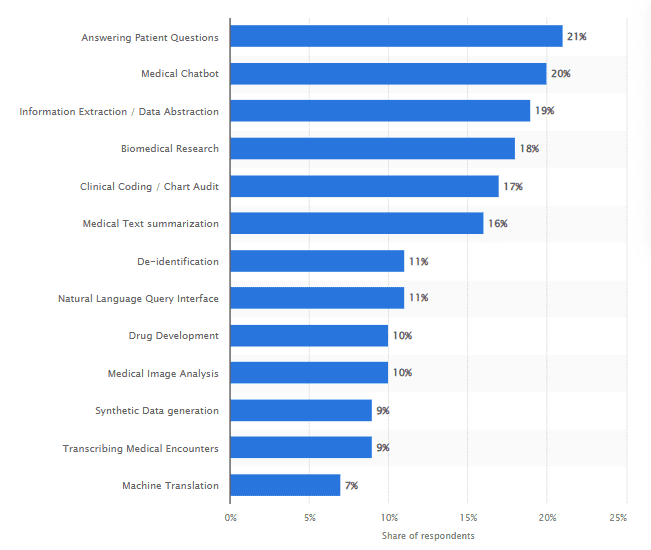
Uses for LLM use in healthcare in the US
15. Accenture’s 2021 study found that language tasks account for 62% of total worked hours, and 65% of these tasks can be automated or augmented with LLMs.
16. Large language models also play a role in financial advising, with nearly 60% of Bank of America’s clients using LLM products for advice on investments, insurance, and retirement plans.
17. According to Arize, 59.1% of technical teams still rely on OpenAI’s LLMs, though Meta’s Llama 2 and other alternatives are gaining popularity.
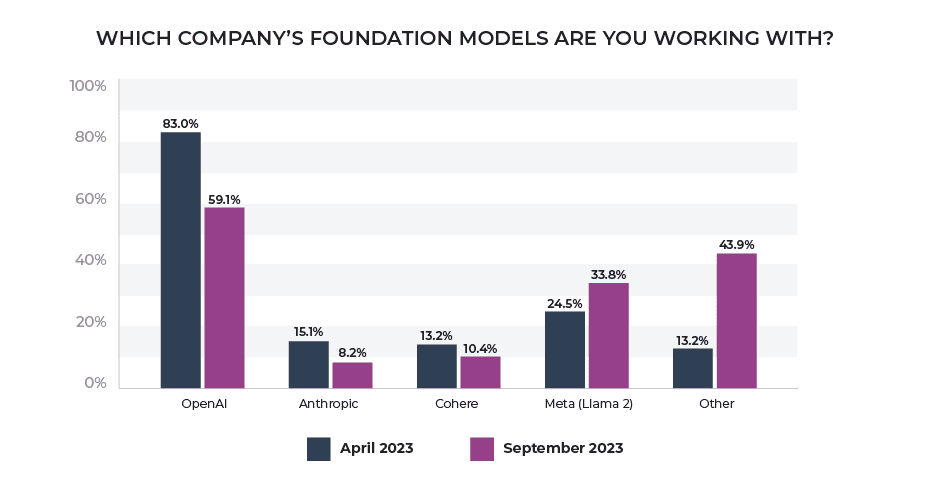
Percentage of the company’s foundation models that technical teams are working with
18. A Datanami survey conducted in August 2023 found that while 58% of companies experiment with LLMs, only 23% have deployed or plan to deploy commercial models.
19. Most teams (60.6%) using LLMs are implementing prompt engineering, and 40.9% are utilizing vector databases. Additionally, 30.1% are leveraging LLM observability tools.
Regional LLM Stats
The global market for large language models (LLMs) is growing rapidly, but the adoption and demand vary across different regions.
Each area has its own pace of growth and is influenced by local technological advancements, industries, and the availability of resources.
While some regions are leading the way in LLM implementation, others are just starting to explore the potential of these powerful AI tools.
Here are some important LLM stats that reveal the regional market size:
20. According to Pragma Market Research, the global LLM market is expected to increase from $1.59 billion in 2023 to $259.82 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 79.80% from 2024 to 2030.
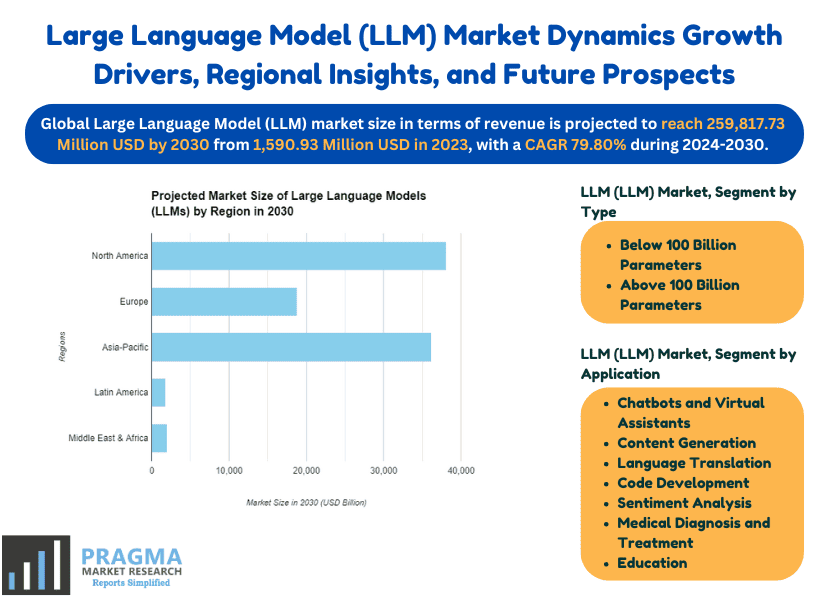
Projected market size of LLM by region in 2030
21. In North America, the LLM market is set to increase from $848.65 million in 2023 to $105.55 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 72.17% during the forecast period.
22. The European market for LLMs is expected to rise from $270.61 million in 2023 to $50.09 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 83.30% from 2024 through 2030.
23. In the Asia-Pacific region, the LLM market is projected to grow from $416.56 million in 2023 to $94.03 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 89.21% over the forecast period.
24. For Latin America, the market is expected to expand from $25.86 million in 2023 to $4.80 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 83.54% during the forecast period.
25. In the Middle East and Africa, the LLM market is estimated to grow from $29.25 million in 2023 to $5.35 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 82.85% from 2024 to 2030.
LLM Scale and Performance Stats
LLM tools are the backbone of the large language model ecosystem.
These tools help businesses, developers, and researchers harness the power of LLMs to create applications, automate tasks, and drive innovation.
From APIs that allow easy access to advanced models to customizable solutions that fit specific needs, LLM tools are becoming essential for anyone looking to implement AI technology.
Here are some key LLM stats that show how the top models are shaping the AI landscape:
26. GPT-4o: The newest model from OpenAI, GPT-4o is faster and even more affordable than its predecessor GPT-4. It generates tokens twice as fast and costs 50% less.
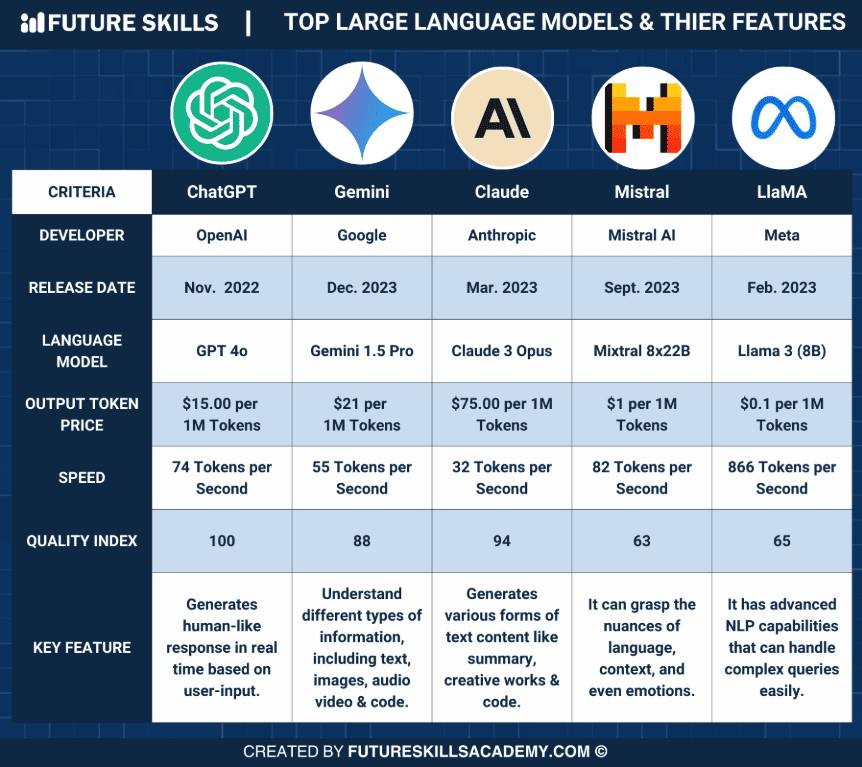
Comparison of top large language models
27. Claude 3.5 Sonnet: Claude is a strong competitor to GPT-4 and ChatGPT. The latest version, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, offers a massive 200,000-token context window, much larger than GPT-4’s 32,000-token capability while keeping costs low.
28. Amazon’s Investment in Anthropic: Amazon has invested over $4 billion in Anthropic, valuing the startup at $15 billion. In May 2024, the Claude mobile app was launched, expanding its reach.
29. Grok-1: Developed by Elon Musk’s xAI, Grok-1 is the largest open-source LLM to date, with 314 billion parameters. In August 2024, xAI also released Grok-2 and Grok-2 mini, with Grok-2 surpassing GPT-4o in various categories like GPQA and DocVQA.
30. PaLM 2: Google’s PaLM 2 model is a major upgrade over its predecessor, PaLM. It’s trained on 3.6 trillion tokens and boasts 340 billion parameters, powering Google’s Bard chatbot.
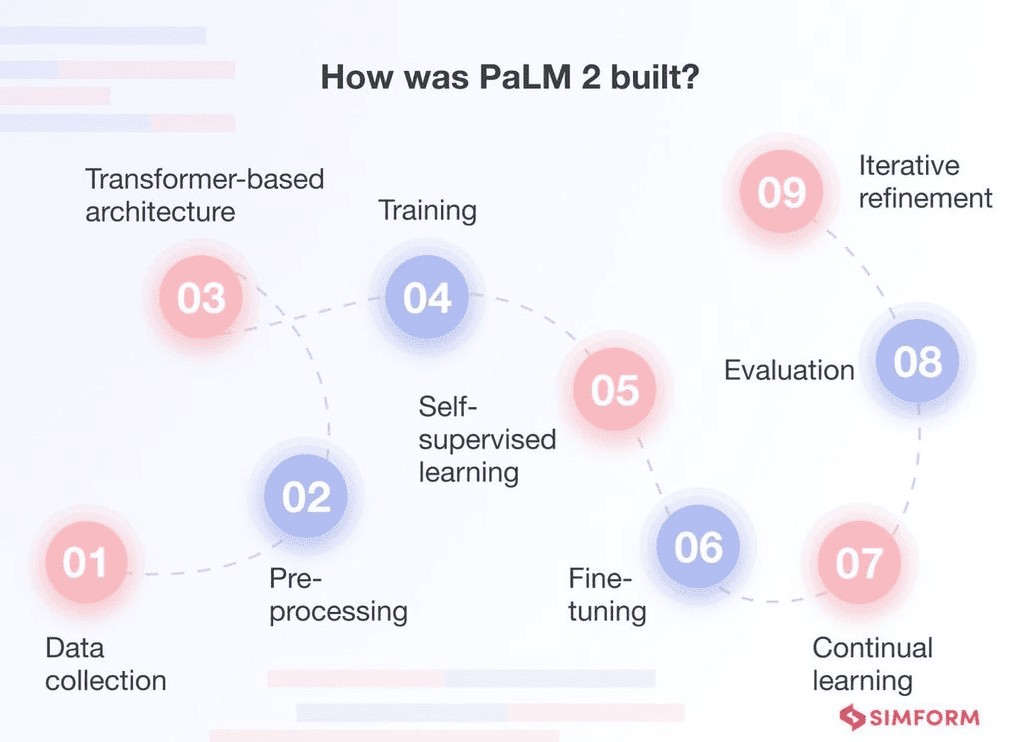
How PaLM 2 was built, step-by-step
31. Falcon 180B: Developed by the Technology Innovation Institute, Falcon 180B is an enhanced version of Falcon 40B, featuring 180 billion parameters, 4.5 times the size of its predecessor.
32. Stable LM 2: Created by Stability AI, the makers of Stable Diffusion, Stable LM 2 includes models like Stable LM 2 12B (12 billion parameters) and Stable LM 2 1.6B (1.6 billion parameters), offering powerful performance.
33. Gemini 1.5: Google’s Gemini 1.5 is an upgraded model with a 1 million-token context window, the largest among current LLMs. It’s available for early testing and offers an impressive range of capabilities.
34. Llama 3: Llama 3, available in 70B and 8B versions, outperformed other open-source models like Mistral 7B and Google’s Gemini 7B in various benchmarks. The latest version, Llama 3.1, boasts 405 billion parameters and an expanded context length of 128,000 tokens.
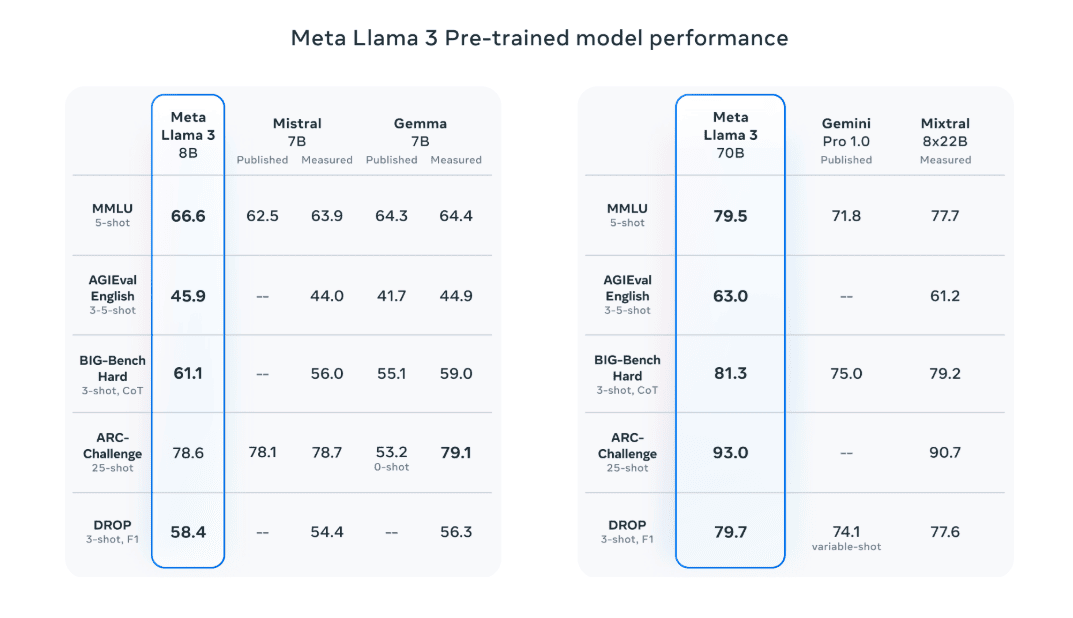
Comparison of Llama 3 with other models
35. Mixtral 8x22B: Mistral AI’s Mixtral 8x22B is a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) model with 141 billion parameters. It activates only 39 billion parameters at a time, optimizing performance and cost.
36. Inflection-2.5: The latest LLM from Inflection AI, Inflection-2.5 powers its conversational assistant, Pi. It achieves over 94% of GPT-4’s average performance while using only 40% of the training effort.
37. Command R: A scalable series of LLMs from Cohere, Command R supports ten languages and a large 128,000-token context window (about 100 pages). It excels in retrieval-augmented generation, code explanations and rewrites, and reasoning tasks.
38. Gemma: Developed by Google DeepMind, the Gemma series consists of lightweight open-source LLMs. With a context window of 8,000 tokens, these models are available in 2 billion and 7 billion parameter sizes and are limited to text-based inputs and outputs.
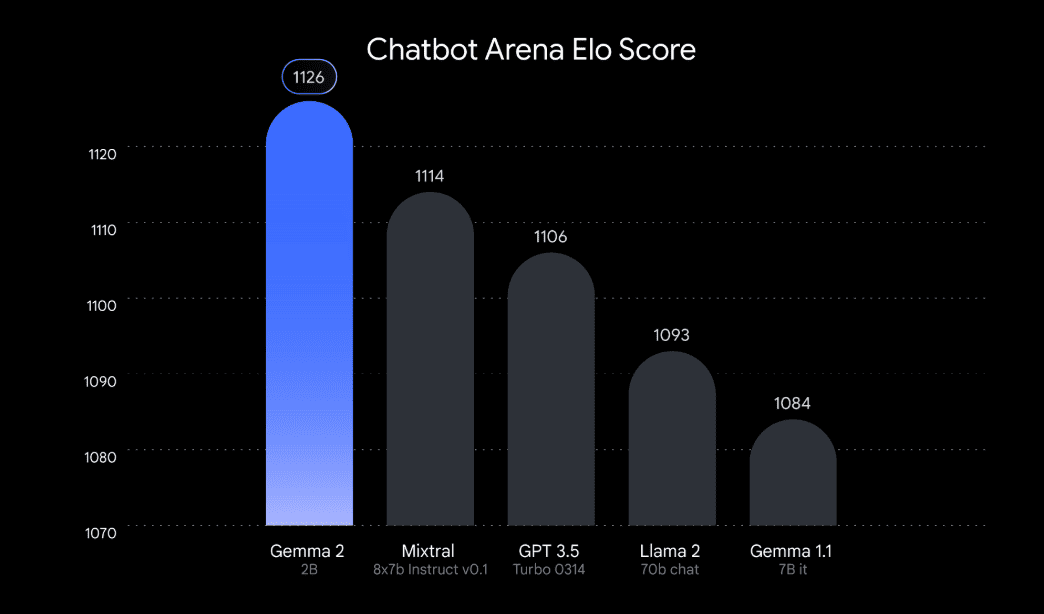
Gemma 2 2B surpasses all GPT-3.5 models on the Chatbot Arena
39. XGen-7B: A large language model from Salesforce, XGen-7B has 7 billion parameters and an 8k token context window. Trained on 1.37 trillion tokens, it uses data from RedPajama, Wikipedia, and Salesforce’s Starcoder dataset.
40. DBRX: Built by Databricks and Mosaic ML, DBRX is an open-source LLM with a mixture-of-experts architecture. It activates 36 billion out of a total of 132 billion parameters for each input.
41. Pythia: A series of 16 LLMs developed by EleutherAI, Pythia offers model sizes from 70 million to 12 billion parameters. As an open-source model, Pythia serves as the base for fine-tuned LLMs like Databricks’ Dolly 2.0.
LLM Funding and Costs Stats
The rapid growth and advancement of large language models (LLMs) have caught the attention of governments, companies, and investors around the globe.
From major investments in AI research to the strategic allocation of funds for LLM development, the financial backing driving this technology is substantial.
As LLMs continue to evolve, they are shaping the future of various industries, attracting millions—if not billions—of dollars in funding.
Here are some important stats and how different countries and companies are investing in AI:
42. The United States leads in AI investment, spending a total of $328.5 billion over the last five years. In 2023 alone, it spent $67.9 billion, marking a 65.94% increase compared to 2019.
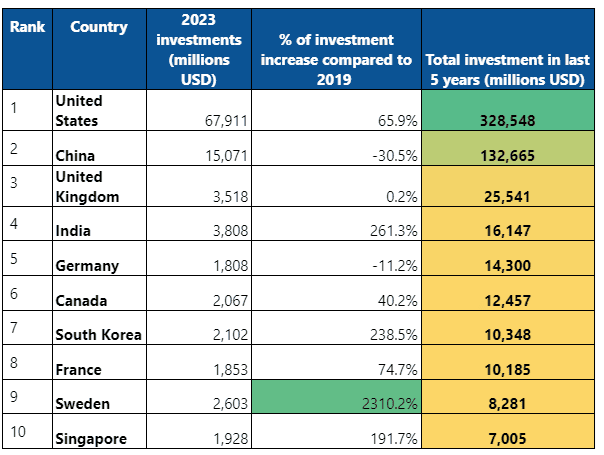
US leads the world in AI business investment
43. China ranks second, with $132.7 billion spent on AI between 2019 and 2023. However, its spending has been slowing down, with a decrease in 2023 ($15.1 billion) compared to 2019.
44. The United Kingdom comes in third, investing $25.5 billion in AI over the same period—almost 13 times less than the US.
45. India takes the fourth spot with $16.1 billion invested in AI over the last five years, surpassing Germany by nearly 13% ($1.8 billion).
46. Sweden shows the most impressive growth in AI investment, with an eye-popping increase of 2310% over the past five years.
47. In 2023, the US also reported the highest number of newly funded AI companies, with 897 new startups, while China followed with 122.
48. Private investments have dominated global AI spending, with mergers and acquisitions leading the charge in 2021, reaching $173.4 billion. In 2020, minority stake investments accounted for $86.4 billion.
49. From 2013 to 2023, the US led in newly funded AI companies, with 5,509 companies, more than 4,000 ahead of the UK, which ranked second.
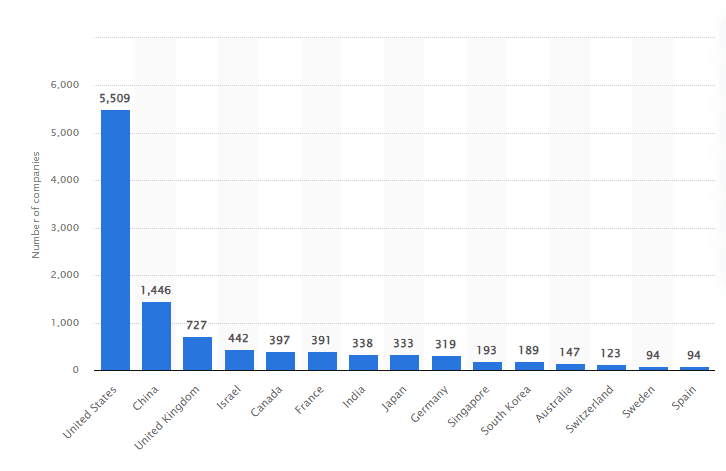
Total number of newly funded AI companies worldwide, by region
50. The US has also contributed the largest share of private AI investments, with over $336 billion, followed by China at $104 billion.
51. In 2023, the US accounted for the majority of global private AI investments, with $67.2 billion, leaving China far behind at $7.8 billion.
52. OpenAI, known for ChatGPT, remains the most heavily funded LLM developer globally in 2023, following the surge in interest from the generative AI revolution.
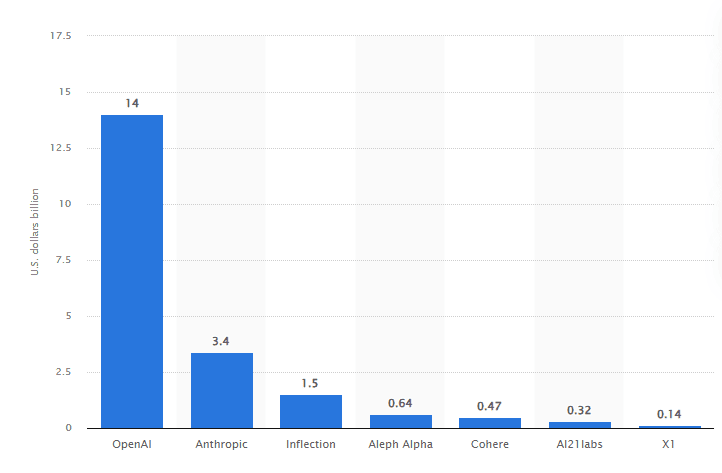
LLM artificial intelligence developer funding globally in 2023
53. Anthropic, a rising AI startup, secured the largest equity deal of 2023, attracting $2.15 billion in funding, mainly from Google and Amazon, as they try to catch up with Microsoft and OpenAI.
54. The US government has steadily increased its spending on AI, machine learning, and autonomy, with its budget growing from $1.38 billion in 2018 to $3.33 billion by 2023.
Conclusion
As the demand for LLM solutions continues to grow, so do the expectations surrounding their abilities.
People increasingly see them as intelligent machines capable of doing anything.
However, these high expectations have led to disappointment, as these models still need improvement.
While it’s true that LLMs are versatile—after all, we wouldn’t be seeing so many LLM usage stats if they weren’t—they still have a long way to go.
It’s easy to forget this when looking at products like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, but large language models still struggle with issues like hallucinations, biases, and inaccuracies.
But one thing is totally clear: LLM adoption is here to stay, and it’s not just a passing trend.


